User:LABoyd2/2D objects 150919
square
[edit | edit source]Creates a square or rectangle in the first quadrant. When center is true the square is centered on the origin. Argument names are optional if given in the order shown here.
square(size = [x, y], center = true/false); square(size = x , center = true/false);
- parameters:
- size
- single value, square with both sides this length
- 2 value array [x,y], rectangle with dimensions x and y
- center
- false (default), 1st (positive) quadrant, one corner at (0,0)
- true, square is centered at (0,0)
- size
default values: square(); yields: square(size = [1, 1], center = false);
- examples:
equivalent scripts for this example square(size = 10); square(10); square([10,10]); . square(10,false); square([10,10],false); square([10,10],center=false); square(size = [10, 10], center = false); square(center = false,size = [10, 10] );
equivalent scripts for this example square([20,10],true); a=[20,10];square(a,true);
circle
[edit | edit source]Creates a circle at the origin. All parameters, except r, must be named.
circle(r=radius);
- Parameters
- r : circle radius. r name is the only one optional with circle.
- circle resolution is based on size, using $fa or $fs.
- r : circle radius. r name is the only one optional with circle.
- For a small, high resolution circle you can make a large circle, then scale it down, or you could set $fn or other special variables. Note: These examples exceed the resolution of a 3d printer as well as of the display screen.
scale([1/100, 1/100, 1/100]) circle(200); // create a high resolution circle with a radius of 2. circle(2, $fn=50); // Another way.
- d : circle diameter (only available in versions later than 2014.03. Debian is currently know to be behind this)
- $fa : The angle (in degrees) from one fragment to the next. See OpenSCAD_User_Manual/Other_Language_Features.
- $fs : The circumferential length of each fragment. See OpenSCAD_User_Manual/Other_Language_Features.
- $fn : The fixed number of fragments to use. See OpenSCAD_User_Manual/Other_Language_Features.
defaults: circle(); yields: circle($fn = 0, $fa = 12, $fs = 2, r = 1);
equivalent scripts for this example circle(10); circle(r=10); circle(d=20);
ellipse
[edit | edit source]An ellipse can be created from a circle by using either scale() or resize() to make the x and y dimensions unequal. See OpenSCAD User Manual/Transformations
equivalent scripts for this example resize([30,10])circle(d=20); scale([1.5,.5])circle(d=20);
regular polygon
[edit | edit source]A regular polygon of 3 or more sides can be created by using circle() with $fn set to the number of sides. The polygon is inscribed within the circle with all sides (and angles) equal. One corner points to the positive x direction. For irregular shapes see the polygon primitive below.
script for these examples
translate([-42, 0]){circle(20,$fn=3);%circle(20,$fn=90);}
translate([ 0, 0]) circle(20,$fn=4);
translate([ 42, 0]) circle(20,$fn=5);
translate([-42,-42]) circle(20,$fn=6);
translate([ 0,-42]) circle(20,$fn=8);
translate([ 42,-42]) circle(20,$fn=12);
color("black"){
translate([-42, 0,1])text("3",7,,center);
translate([ 0, 0,1])text("4",7,,center);
translate([ 42, 0,1])text("5",7,,center);
translate([-42,-42,1])text("6",7,,center);
translate([ 0,-42,1])text("8",7,,center);
translate([ 42,-42,1])text("12",7,,center);
}
polygon
[edit | edit source]Creates a multiple sided shape from a list of x,y coordinates. A polygon is the most powerful 2D object. It can create anything that circle and squares can, as well as much more. This includes irregular shapes with both concave and convex edges. In addition it can place holes within that shape.
polygon(points = [ [x, y], ... ], paths = [ [p1, p2, p3..], ...], convexity = N);
Parameters
- points
- The list of x,y points of the polygon. : A vector of 2 element vectors.
- Note: points are indexed from 0 to n-1.
- paths
- default
- If no path is specified, all points are used in the order listed.
- single vector
- The order to traverse the points. Uses indices from 0 to n-1. May be in a different order and use all or part, of the points listed.
- multiple vectors
- Creates primary and secondary shapes. Secondary shapes are subtracted from the primary shape (like difference). Secondary shapes may be wholly or partially within the primary shape.
- default
- A closed shape is created by returning from the last point specified to the first.
- convexity
- Integer number of "inward" curves, ie. expected path crossings of an arbitrary line through the polygon. See below.
defaults: polygon(); yields: polygon(points = undef, paths = undef, convexity = 1);
Examples:
equivalent scripts for this example polygon(points=[[0,0],[100,0],[130,50],[30,50]]); polygon([[0,0],[100,0],[130,50],[30,50]], paths=[[0,1,2,3]]); polygon([[0,0],[100,0],[130,50],[30,50]],[[3,2,1,0]]); polygon([[0,0],[100,0],[130,50],[30,50]],[[1,0,3,2]]); . a=[[0,0],[100,0],[130,50],[30,50]]; b=[[3,0,1,2]]; polygon(a); polygon(a,b);
equivalent scripts for this example polygon(points=[[0,0],[100,0],[0,100],[10,10],[80,10],[10,80]], paths=[[0,1,2],[3,4,5]],convexity=10); . triangle_points =[[0,0],[100,0],[0,100],[10,10],[80,10],[10,80]]; triangle_paths =[[0,1,2],[3,4,5]]; polygon(triangle_points,triangle_paths,10);
The 1st path vector, [0,1,2], selects the points, [0,0],[100,0],[0,100], for the primary shape. The 2nd path vector, [3,4,5], selects the points, [10,10],[80,10],[10,80], for the secondary shape. The secondary shape is subtracted from the primary ( think difference() ). Since the secondary is wholly within the primary, it leaves a shape with a hole.
example polygon with multiple holes a0 = [[0,0],[100,0],[130,50],[30,50]]; b0 = [[1,0,3,2]]; a1 = [[20,20],[40,20],[30,30]]; b1 = [[4,5,6]]; a2 = [[50,20],[60,20],[40,30]]; b2 = [[7,8,9]]; a3 = [[65,10],[80,10],[80,40],[65,40]]; b3 = [[10,11,12,13]]; a4 = [[98,10],[115,40],[85,40],[85,10]]; b4 = [[14,15,16,17]]; a = concat (a0,a1,a2,a3,a4); b = concat (b0,b1,b2,b3,b4); polygon(a,b);
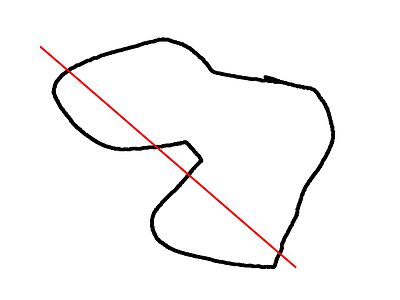
convexity
The convexity parameter specifies the maximum number of front sides (back sides) a ray intersecting the object might penetrate. This parameter is only needed for correctly displaying the object in OpenCSG preview mode and has no effect on the polyhedron rendering.
This image shows a 2D shape with a convexity of 4, as the ray indicated in red crosses the 2D shape a maximum of 4 times. The convexity of a 3D shape would be determined in a similar way. Setting it to 10 should work fine for most cases.