Plastics Molding & Manufacturing/Pressure
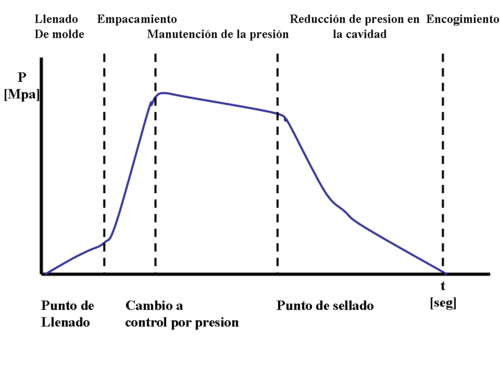
There are 3 types of pressure parameters that will be focused here : injection pressure , holding pressure and clamping pressure
Injection Pressure
[edit | edit source]Injection pressure can be defined as the amount of pressure required to produce the initial filling of the mold cavity image.Initial filling represents approximately 95% of the total filling of the cavity image. It is determined by the viscosity of melted plastics and flow rate of the plastic being injected. Of the more than 20,000 plastic materials available today, most will fall within a pressure range of 30,000 kPa to 100,000 kPa
Holding Pressure
[edit | edit source]Holding pressure can be defined as pressure against the cooling plastic in the cavity image while that plastic solidifies.It is used for the final 5% filling of the cavity image. This will helps to ensure a dense part, molded with uniform pressure and controlled shrinkage.
Clamping Pressure
[edit | edit source]Clamp pressure can be defined as the amount of pressure required to hold the mold closed against injection pressure. The amount of pressure applied must be at least equal to the amount of pressure applied by the injection unit. The pressure of the clamping must be greater than the injection pressure as to prevent the built up of plastic materials inside the cavity will pushes the clamping slightly that may causes flashes. However, if the clamp pressure is too great, the mold may collapse from the total force being applied.
In conclusion:
If pressure ↑ , thinner cavity can be filled more easily but can introduces flashes and increase internal stress
If pressure ↓ , internal stress can be reduced but can introduces short filling and also uneven shrinkage
