Chemistry for Idiots, Humans and Rebels/Printable version
| This is the print version of Chemistry for Idiots, Humans and Rebels You won't see this message or any elements not part of the book's content when you print or preview this page. |
The current, editable version of this book is available in Wikibooks, the open-content textbooks collection, at
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Chemistry_for_Idiots,_Humans_and_Rebels
The Basics
So, what's the deal with Chemistry?
Well, think back to the old Lego set from childhood. There were several kinds: some were two bumps wide, others one bump wide, some were six or eight or ten bumps long, and others were four or even two. There was even a one by one. With these combinations and a little imagination, you could build virtually anything.
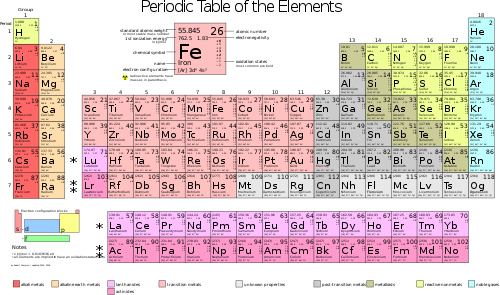
Chemistry is like an advanced Lego set, but with a lot more types of pieces. To be exact, there are 118 known elements to date. An element is a type of atom, like iron (element #26) or hydrogen (element #1) or potassium (element #19). These are the "Lego bricks" of chemistry.
You can find a complete list of all the elements in a special kind of table called "the Periodic Table of the Elements." Here is a link to a periodic table: www.ptable.com. This shows all 118 known elements, and puts them into columns by their properties.
In each vertical column, the elements are similar in some way. For example, in the furthest left column, Hydrogen (#1), Lithium (#3), Sodium (#11), Potassium (#19), and numbers 37, 55, and 87, all share the property of being highly reactive. They don't play well with others. Sodium, in water, will explode violently. Hydrogen is extremely flammable. Lithium is mildly explosive. But the column on the extreme right consists of the "Noble Gases." They are all "noble" because they tend not to mix with other elements. They are the opposite of reactive. In fact, #18, Argon, is sometimes used to protect reactive elements from exposure to oxygen.
You will notice that each element has an abbreviation, or symbol. For example, Hydrogen is H. Argon is Ar. Lithium is Li. Those all seem to make sense. But the symbol for iron is Fe, and for Potassium is K. This is because these elements were known to the ancient scientists, and are called by their Latin names -- Ferrum, for iron, and Kalium, for Potassium. Every element that was known in classical times is called by the abbreviation of its Latin name, and those that have only been discovered in more modern times are known by their English names.
Scientists put these abbreviations together into "formulas" which are like the diagram of a spaceship on the outside of the Lego box. If you follow the directions, you can make the compound. For example, 2 Hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom create a formula H2O. That formula is a compound that we call "Water." Another common compound is NaCl (one sodium atom plus one chlorine atom makes table salt, or NaCl). When we put two or more different elements together, we call it a molecule.
Another common formula is C12H22O11. Twelve carbon atoms, plus twenty-two hydrogen atoms, plus eleven oxygen atoms form one molecule of sugar. As you can imagine, the more atoms that it takes to make a molecule, the "heavier" that molecule is compared to others. A molecule of sugar takes 45 atoms, and a molecule of water takes 3. As you can imagine, sugar sinks when placed in water.
But when considering the "weight" of a molecule, we also have to consider that each atom on the Periodic Table has a different weight. The "Atomic number" of the atom gives us a rough estimate of the weight of the atom. For example, Hydrogen is #1, and Carbon is #6. As you might imagine, Carbon weighs more than Hydrogen -- about 12 times as much. Carbon weighs almost exactly 12 Atomic Mass Units. Oxygen, #8, weighs almost exactly 16 Atomic Mass Units.
These proportions -- 6/12, and 8/16, should give you a clue about each of these atoms. Clearly, the weight is roughly double the Atomic number. But Hydrogen has a weight of roughly 1 AMU. To understand this, we need to see what an atom is like. An atom has a core, made up of protons and neutrons. Smaller particles called "electrons" orbit the nucleus. Each element has as many protons as its Atomic number. Most have the same number of neutrons, also, making the weight of the element roughly twice the atomic number in many cases. Electrons have very little weight (1/1840) -- almost not enough to matter in these weights.
So Carbon, then, has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in each nucleus, for an atomic weight of almost exactly 12. It also has 6 electrons. Oxygen has 8 protons, and 8 neutrons -- that's the atomic weight of 16 -- plus eight electrons.
But there are also "odd cousins" in each element's family. For example, some Carbon atoms have two extra neutrons, making a count of 6, 8, and 6. These two extra neutrons make the carbon atom weight 14 AMU instead of 12, so we call it "Carbon 14," and we refer to the ordinary common carbon as "Carbon 12." Most carbon that we find in nature is about 98.9% Carbon 12, 1.1% Carbon 13 (which, as you might guess, has one extra neutron), and less than .1% Carbon 14. There are other types of carbon -- we call variations of an element "Isotopes" -- but the other isotopes of Carbon are extremely rare.
Of the 118 elements that we mentioned on the Periodic Table, some are very rare, and some can only be made by smashing other atoms together and making them stick. All of the atoms with Atomic numbers above 85 (Astatine) are rare, and those with atomic numbers above 94 (Plutonium) are mostly man-made, through nuclear processes or by slamming other atoms together. All of the elements above 83 (Bismuth) are considered radio-active, meaning that they "decay" into other elements. For example, a Uranium (#92) atom will often split into a helium (#2) atom and a Thorium (#90) atom.
Periodic Table of Elements
Mole Concept
Text
[edit | edit source]Need a textbook like introduction here.
Chemistry can be a daunting subject for even the best students, and let's face it, statistically, most of us are not the best students. Fortunately for us, there is hope! Chemistry does not have to be a giant confusing pit of pain and despair if we take just a few minutes to break down and understand what the Chemist's mumbo-jumbo ACTUALLY means. "Chemistry for Idiots, Humans and Rebels" is here to provide a resource that explains Chemistry plainly, nicely, and with application.
Here are the topics that have to be included (not an exhaustive list!):
(Please note that the pages on the following topics have been copied from wikipedia. See the talk page for more details!)
Themes and Outline
[edit | edit source]Atomic Mass Unit
[edit | edit source]Outline : -
- What is mass? What is atomic mass? (Preferably with a "duh" style) (for idiots)
- Mass Number and atomic mass, the subtle difference. Introduce weighted average. Need a sample problem.
- An "investigatory" text - asking the students to look at a table and figure out why Carbon does not have exact 12 as its atomic mass number, but C12 HAS! Introduce C14!
- A good reference here can be to carbon 14 - how it matters in carbon dating. Plus more on isotopes and add "see also" links.
- Definition of the AMU
- Make the reader "feel" the difference between amu and grams!
- Sample problems making clear the following facts :
- relation between amu and C12 isotope
- Mass Number and atomic mass
- ...
Molecular Mass
[edit | edit source]- Molecular mass = mass of the molecule! (Duh statement again!)
- Maybe a nice way to introduce this would be to question the reader!
- What about stuff that is not molecule? Formula mass!
- Sample problems on molecular mass.
- Need to have a good description, with an analogy to packages and possibly pop references.
- For example a combo meal, or a gadget combo, anything. This is for:
- Keeping the students awake!
- Making them think about the introduced topics rather than just serve it to them on a platter!
- Note : If anyone someday starts collaborating on this project, we will have to figure out a way for streamlining inputs on text boxes, main text, sample problems, illustrations etc.
Justification
[edit | edit source]A lot of people might not agree with what I have said. A lot of them might counter argue by saying that this is too much, that formula mass/molecular mass is pretty straightforward! Yes it is and yet there is a problem. People fail to imagine it properly. People fail to realiza that it is nothing but elementary calculation that they have already been doing since ages, only difference being that the things in the word problem have different names now!
- This in itself might be a good text box!
Sample Problems
[edit | edit source]Molecular masses of water, liquid bromine, sugar, salt and other such relevant and "exotic compounds!
Note : Someone actually needs to start typing these problem sets! That might be me, that might be someone else who comes in at a later stage in the preparation of this book!
The Mole
[edit | edit source]- The mole is the standard unit of measurement, under the International System of Units (SI), for amount of substance. It is defined as the amount of chemical substance that contains as many representative particles as in 12 grams of Carbon-12.
- Tell them bluntly in simpler English.
- Ask questions to the reader, that force him to think about the simple terms in the definition.
- question 1
- question 2
- question 3
- Add a few introductory questions to exercise their brains, avoiding TMI/Too Much Information!
- Difference between number of atoms and moles of atoms.
- Avagadro's number and dozen, scores, tens, hundreds, lacs. Possibly a good place for a cartoon.
**Cartoon!
Introductory Questions
[edit | edit source]- How big Avagadro's number is!
- How small atoms are!
- Conversions!
Concentration and amount
[edit | edit source]- Expand on the case of hot chocolate. More chocolatey and more chocolate powder needed. Good way to introduce concentration and relate it with molalities. (for idiots)
- Keep this a recurring theme throughout the intro text and in a few problems.
- More acid (can react with more base) and more acidic is a good example.
- More base and more basic.
- More colour required vs. more strongly coloured solution
- Keep this a recurring theme throughout the intro text and in a few problems.
- Need some sample problems! (for humans)
- A box text can be to introduce and relate to density, specific gravity, cost and extrapolating to intrinsic and extrinsic properties. (for rebels)
- Molarity Vs. Molality : The whole deal about thermal expansion. (for humans) and their implications in thermodynamics and a few interesting examples (for rebels)