Applied Science BTEC Nationals/Chemical Laboratory Techniques/Ethanal
| Read Wikibooks:Risk disclaimer before attempting anything on this page. Some of the information here may be incorrect, unverified, and dangerous. Wikibooks, the WMF and the contributors accept no liability for the content of this page. |
The experiments are written for experienced science teaching staff to use as instructions for a supervised class of students. The experiments are not designed for students or inexperienced members of the public to perform without supervision. If you wish to attempt the experiments, ensure that you have completed a legally adequate risk assessment beforehand and that you work within the constraints of the risk assessment.
Theory
[edit | edit source]Ethanol can be oxidised by the dichromate (VI) ion in acidic solution. The first product of the oxidation is ethanal, which can be further oxidised to form ethanoic acid. By carefully changing the reaction method, one or other product can be obtained.
The ethanal preparation should be performed in a fume cupboard.
Chemicals
[edit | edit source]- sodium dichromate (VI)
- ethanol
- ethanal (product)
- concentrated sulphuric acid
- anti-bumping granules
- deionised water
Precautions
[edit | edit source]Wear eye protection and laboratory coat.
Work in the fume cupboard when preparing ethanal.
Wear gloves when taking samples of concentrated sulphuric acid
Method
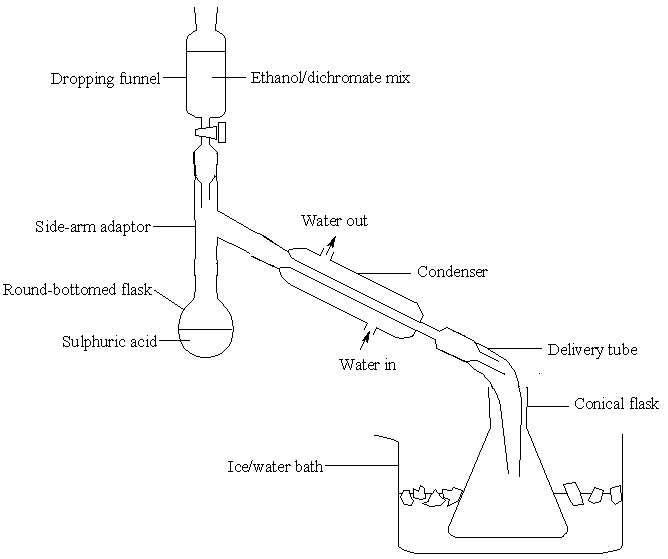
[edit | edit source]Into a round-bottomed flask, add first 50 cm3 deionised water and then 17 cm3 concentrated sulphuric acid. Add the acid slowly, with shaking. Finally, add some anti-bumping granules to the flask and set up the apparatus shown below:
There should be rapid flow of water round the condenser. Ask your lecturer to adjust the flow if you do not feel confident – it is easy to create too much pressure in the rubber tubes. Dissolve 50 g sodium dichromate (VI) in 50 cm3 deionised water and then add 40 cm3 ethanol. Mix well and add the mixture to the dropping funnel in the above apparatus. Ensure the tap is closed first.
Heat the acid in the flask until it boils gently, then turn off the heat.
Add the ethanol/dichromate mixture slowly: allow 20 minutes for adding the entire sample. The reaction is vigorous and will keep the mixture boiling at first. In the latter stages of the reaction you will have to heat the mixture to keep it boiling gently.
While the reaction occurs in the round-bottomed flask, ethanal solution will collect in the conical flask.
Cautiously note its characteristic smell. Stopper the flask and keep it in iced water. If you have time, take samples and test using the silver mirror, 2,4-DNPH or iodoform tests.