GCSE Computing/network topologies
Network Topologies[edit | edit source]
Meaning[edit | edit source]
To form a network it is necessary to connect computers together. There is more than one way that this can be done. You need to know about the following three types:
Types[edit | edit source]
Bus Network[edit | edit source]

In local area networks where bus topology is used, each machine is connected to a single cable. Each computer or server is connected to the single bus cable through some kind of connector. A terminator is required at each end of the bus cable to prevent the signal from bouncing back and forth on the bus cable. A signal from the source travels in both directions to all machines connected on the bus cable until it finds the MAC address or IP address on the network that is the intended recipient. If the machine address does not match the intended address for the data, the machine ignores the data. Alternatively, if the data does match the machine address, the data is accepted. Since the bus topology consists of only one wire, it is cheap to implement compared to other topologies. However, there is a higher cost of managing the network. Additionally, since only one cable is used, so if that network cable breaks the entire network will be down
Ring Network[edit | edit source]
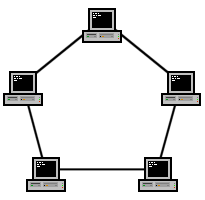
A network topology that is set up in a circular fashion in which data travels around the ring in one direction and each device on the right acts as a repeater to keep the signal strong as it travels. Each device incorporates a receiver for the incoming signal and a transmitter to send the data on to the next device in the ring. The network is dependent on the ability of the signal to travel around the ring
Star Network[edit | edit source]

In local area networks with a star topology, each network host (for example a PC) is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection. All traffic on the network passes through the central hub. The hub acts as a signal booster or repeater. The star topology is considered the easiest topology to design and implement. An advantage of the star topology is the simplicity of adding additional nodes. The primary disadvantage of the star topology is that it may need a lot more cables, and if the hub breaks everything will stop working.