Wikijunior:Biology/Cells
Cells
[edit | edit source]
All living things are made of cells. They are the components and building blocks of life.
What is a cell? A cell is a bag of liquid that holds in the stuff of life.
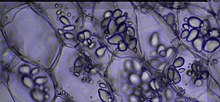
A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of a living organism. The word "cell" comes from the Latin word cella, which means small room. If you look at living things under a microscope, you will see that they are made of small squares or balls. Robert Hooke, a biologist from England, saw these small squares in a hard material called cork using a microscope in the year 1665. They looked like rooms, and so he called them cells. He was also the first person to observe dead cells.
What types of cells are there? There are two kinds of cells: eukaryotes, which have a large ball in them called a nucleus, and prokaryotes, which do not.
Most prokaryotes are very small. Two of the six kingdoms, Bacteria and Archea, are made up of prokaryotes. All of the rest of the kingdoms – Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, and Protista – are made up of eukaryotes.
Endosymbiosis Theory
[edit | edit source]Every human being is a living being. But each one is made up of a large number of tiny living things called cells. But that's not all! Smaller creatures live in every cell of our body. The larger cell nourishes the smaller cells inside, and the small cells perform important functions.
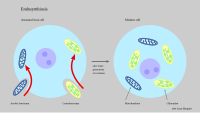
Working together for mutual benefit is called symbiosis. According to the endosymbiont theory, single-celled organisms were taken up by the large cells long ago. The mitochondria are derived from aerobic bacteria. The mitochondria gain energy from food and oxygen. The chloroplasts found in plant cells are derived from cyanobacteria. The chloroplasts gain energy from light.
-
Euglena
-
Euglena
-
Endosymbiosis
-
Endosymbiosis Theory
What do cells look like?
[edit | edit source]Cells are surrounded by a thin layer of oil called the cell membrane. It separates the inside of the cell from the outside. Some cells also have a firm box around them called a cell wall that keeps it from breaking. The water that fills a cell is called the cytoplasm. Inside a cell, knowledge is stored in something called a chromosome. It tells the cell how to work, like steps in a book.
Eukaryotic cells hold their chromosomes in a structure called a nucleus, which has its own oily membrane around it. Cells also have many other things with membranes called organelles, which means "little organs". Some organelles found in eukaryotic cells are called ribosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.

Cells that do different things have different shapes. A plant leaf cell takes light and uses it to make sugar. To do this, it has green organelles called chloroplasts. To get the most light, it pushes cytoplasm in circles around a hollow bubble of water in the center of the cell called a vacuole.
A human sperm cell carries its chromosomes, found in the nucleus, to an egg cell in order to make a new baby. It has a large tail called a flagella that helps it to swim. It also has many organelles called mitochondria that give it power, like how gasoline powers a car.
Types of Organelles
[edit | edit source]- nucleus - A ball of membrane in the middle of the cell that holds the chromosomes.
- chromosomes - Things that hold the knowledge of the cell.
- prokaryote - A cell without a nucleus.
- eukaryote - A cell with a nucleus.
- organelles - Little things inside a cell.
- cytoplasm - The gel-like inside of a cell.
- membrane - An oil bag that holds water.
- vacuole - An organelle full of water and waste inside a cell.
- mitochondria - An organelle that makes power in a cell.
- chloroplast - An organelle that makes sugar found in a plant or protist.
- flagella - A tail on a cell that makes it swim.
- Golgi body - An organelle which helps in secretion.
- ribosome - An organelle which helps in synthesis of proteins.