Science: An Elementary Teacher’s Guide/Elements, atoms, molecules
Introduction: The Building Blocks of Matter
[edit | edit source]Children have a tendency to be curious and may ask many questions. A typical question a child may ask is what is a certain object made from? A child may ask “what is this chocolate cake made of?" A typical answer would be chocolate, milk, sugar, flour etc. Then the child may press on and ask “what is chocolate made of?" You would answer cocoa beans, sugar, butter, milk etc. Now the adult may be in trouble if the child presses on and asks what cocoa beans are made of and if you answer that, the child may keep asking and finally the adult will admit that he does not know. Breaking up a recipe into its ingredients is not difficult, but then breaking up the ingredients further and then breaking up those further is difficult.
What matter is made is an ancient question that has been posed for thousands of years. Greek philosophers reasoned that all matter could be broken up to its simplest component. They called these components "atoms". Of course at that time the idea of the atom could not be proved with evidence and experimentation. It was not until the 19th century that scientists discovered behaviors of matter that could only be explained by the concept of the atom.
Ë===The Atom===
The atom is the smallest particle that composes all matter. It is composed of a nucleus and electrons. There many atoms.....
- Nucleus is in the center
- Protons: in red, have a positive charge and are in the nucleus
- Neutrons: in green, have no charge and are in the nucleus
- Electrons: in yellow, have a negative charge and spin around the nucleus*
- The lights are now back of the day and society of the lecture notes in any way who are the best thing in the world
The matter of anything which occupies space and has mass is called Matt The dawn of civilization
EXPLANATION OF LIQUID PRESSURE ON THE BASIS OF
Molecules
[edit | edit source]A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge. However, in quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the term molecule is often used less strictly, also being applied to polyatomic ions. The atoms of an element can combine to make molecules. A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance that has all of the properties of the substance. All substances are made up of molecules, which are so tiny that only the largest of them can be seen with a powerful electron microscope. Billions of water molecules are contained in a single drop of water. All molecules of a substance are alike and they are different from the molecules of any other substance.

All molecules are constantly moving and striking other molecules. Gas molecules move very rapidly and they are far apart. In a liquid, the molecules move more slowly and are much closer together, but still move around relatively freely. the molecules in a solid seem to just move back and forth, or vibrate, in place since they are closely packed together.
Examples of Molecules:
Water: Has two hydrogen and one oxygen atom.
Carbon Dioxide: Has one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
They also make up most of the oceans and atmosphere. However, the majority of familiar solid substances on Earth, including most of the minerals that make up the crust, mantle, and core of the Earth, contain many chemical bonds, but are not made of identifiable molecules. Also, no typical molecule can be defined for ionic crystals (salts) and covalent crystals (network solids), although these are often composed of repeating unit cells that extend either in a plane or three-dimensionally (such as in diamond, quartz, or sodium chloride). The theme of repeated unit-cellular-structure also holds for most condensed phases with metallic bonding, which means that solid metals are also not made of molecules. In glasses (solids that exist in a vitreous disordered state), atoms may also be held together by chemical bonds without presence of any definable molecule, but also without any of the regularity of repeating units that characterizes crystals.
Elements
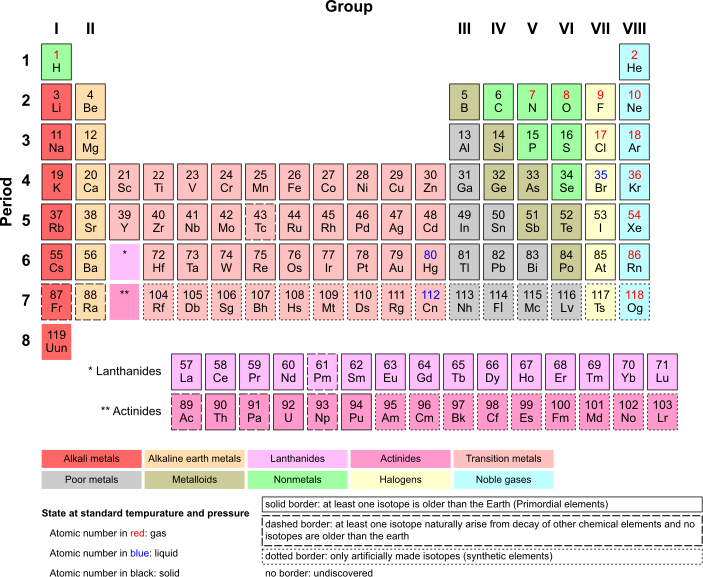
[edit | edit source]Elements are often called the building blocks of matter. All matter is made of atoms. An element is matter that can not be broken up into other elements. All different elements have different number of protons and electrons. These elements are organized in a table called The Periodic Table of Elements. There are currently 109 known elements. The position of any particular element on the Periodic Table is based on certain characteristics of the element. Columns of elements in the Periodic Table, for instance, have similar chemical properties.
The Periodic Table of Elements
- Compound is when two or more different kinds of atoms chemically combine to form a new substance.
- has its own physical and chemical properties
- different properties from those of the elements from which it was formed
-ex: water (two hydrogens atoms mixed with one oxygen atom)
- Mixture is when two or more elements or compounds coexist without combining chemically.
- elements remain separate and distinct
- each retains its own physical and chemical properties
-ex: salt mixed with pepper
- Solution is when a mixture of two substances results in the molecules of one substance being spread out evenly and equally between the molecules of the other substance.
- many common solutions involve a solid dissolved into a liquid
- the solid is called a solute and the liquid is called a solvent; the solute dissolves into the solvent
-ex: soda water (carbon dioxide mixed in water)