Principles of Economics/S-D Shifts
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
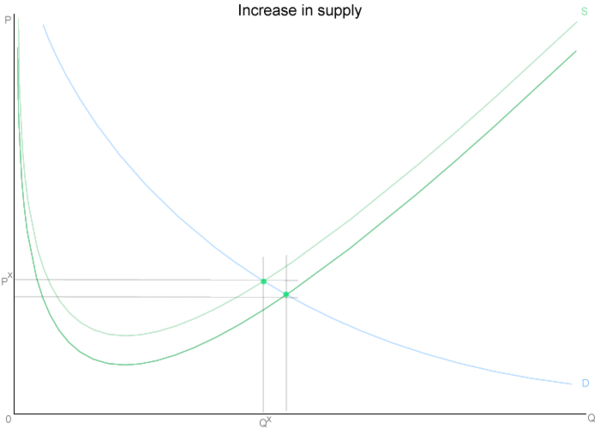
Shift in supply
[edit | edit source]If the supply curve increases (such as an excise tax burden), the new equilibrium will have higher quantity and lower price; if it is lowered, the reverse happens.
Shift in demand
[edit | edit source]If the demand curve increases (such as something being in fashion), the new equilibrium will have higher quantity and higher price; if it is lowered, the reverse happens.
Shift in supply and demand
[edit | edit source]If both curves shift, their individual effects are added, although with slight alterations due to warping in the shape of the curves. If both curves increase, quantity increases for sure but price is indeterminate; if both curves decrease, quantity decreases for sure but price is indeterminate.