GNU Health/Localization
Translating GNU Health
[edit | edit source]The language of the GNU Health user interface is controlled through gettext language packs.
Language packs are are managed, stored and distributed through an online translation platform. This makes maintaining translations easier and faster, and it makes your GNU Health installation leaner, since it contains only the languages needed by your health institution.
The official GNU Health translation portal is now hosted at Weblate
There is a mailing list for all translation related discussions at https://lists.gnu.org/mailman/listinfo/health-i18n . If you are a GNU Health translator, you should subscribe to this mailing list.
When translating GNU Health to your language, please start from the health module which contains the core of GNU Health.
Installation of Language Packs
[edit | edit source]We will go through an example on how to enable the Spanish language and to install the language pack. For this example, we will work on the demo database gnuhealth_demo_generic.
Step 1: Declare your language and make it translatable. This can be done in the Administration → Localization → Languages section.
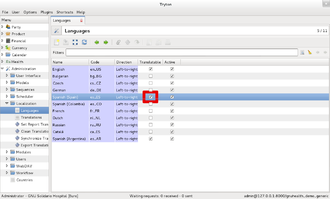
Remember the code of the language (in this case es).

Step 2: Download and uncompress the language pack file for your language and for the specific resource from the translation server.
With the GNU Health administrator user (gnuhealth) execute the following commands .
Note : Substitute the language sample code (es) by your language.
The language files that are retrieved come from development translation server! The official version and languages are shipped in the standard installation. Always try in a development environment before use in production.This overwrites the existing translation files ! |
./gnuhealth-control getlang es
This installs all the modules translation files for the Spanish Spain (es) language.
Step 3: Change your user preferences to your new language:
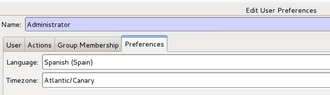
Step 4: Log out and stop your GNU Health Tryton server (if it's running).
Step 5: Update your GNU Health instance with the command
./trytond-admin --all --database=gnuhealth_demo_generic
Step 6: Start your sever with the new language for your module installed.
Setting the User Language
[edit | edit source]Please remember that the language is a user preference. In the same database, you can have different users using different languages.