Biology, Answering the Big Questions of Life/cell division2
| INTERMEDIATE |
Mitosis is a form of cell division which produces two daughter cells from a mother cell. It consists of 4 phases of division: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.

Before Mitosis
[edit | edit source]The period in the cell cycle before mitosis takes up the bulk of a cell's life and is called interphase. Interphase can be split into three periods: G1, S, and G2. G1 and G2 are periods during which cellular processes continue as normal, while the S phase is when DNA is replicated.
During much of mitosis, DNA is wrapped and condensed into chromosomes (pictured). However, during this phase, DNA is uncondensed, and remains in the nucleus as a mass of chromatin, or a combination of DNA and proteins that the DNA wraps around.
Some cells, such as muscle cells or nerve cells, do not replicate after they become specialized during embryonic development. These cells are sometimes said to be in the G0 phase.

Prophase
[edit | edit source]
During prophase, the longest phase of mitosis, the nuclear membrane of the cell begins to disintegrate, and the nucleolus disappears. A centrosome -- an organelle that produces microtubules -- moves to each side of the cell. The DNA begins to condense into chromosomes. Because all the DNA has been replicated already, each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids which have identical DNA. The two sister chromatids of a chromosome are connected in the center of the chromosome, called the centromere. Microtubules called spindle fibers begin extending from the centrosomes and begin to attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes, which are at the centromeres (centers) of the chromosomes.
Note that a centrosome and a centromere are different. A centrosome is an organelle that produces microtubules that attach to the chromosomes, while a centromere is the center of a chromosome that connects two sister chromatids.

Metaphase
[edit | edit source]During metaphase, the chromosomes, which each have two spindle fibers connected to them, line up in the center of the cell. The centromeres at this point are at opposite sides of the cell and have a spindle fiber attached to each chromosome. Some spindle fibers connect in the middle. They will help to push the cells apart.
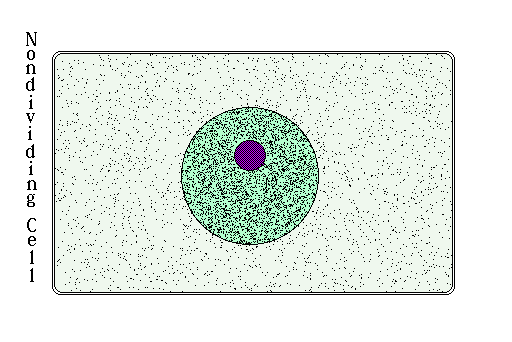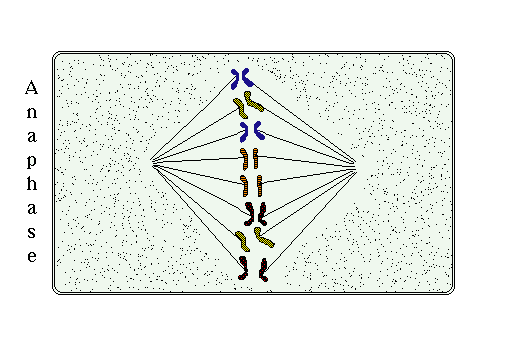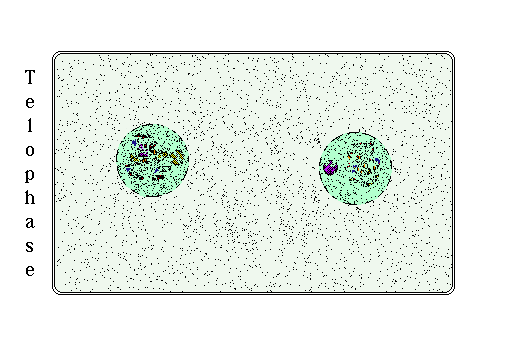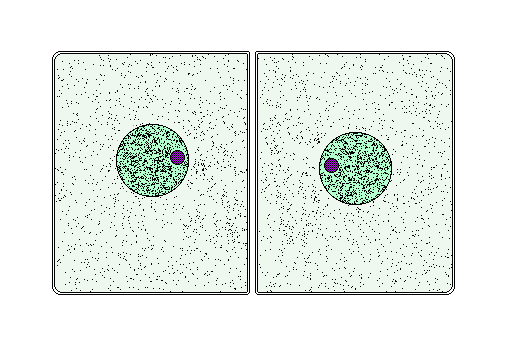
Anaphase
[edit | edit source]During anaphase, the chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. A single copy of an organism's DNA should reside on each side of the cell. Anaphase is usually the shortest phase of mitosis
Telophase
[edit | edit source]During telophase, two new nuclei form around the two sets of DNA, and the chromosomes will unravel into a mass of chromatin that is more convenient for the normal tasks of a cell. The centromeres duplicate so that each daughter cell will have two centromeres.
Cytokinesis is a separate process that is often combined with telophase. Cytokinesis is the splitting of the cytoplasm; the cell physically divides into two new cells. Sometimes, cytokinesis fails to occur, resulting in a large cell with multiple nuclei. This occurs naturally in some tissues, as in liver, and skeletal muscle cells.