A-level Chemistry/OCR (Salters)/Medicines by Design
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
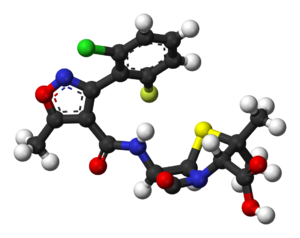
Flucloxacillin is a penicillin antibiotic that used to control resistant Staphylococcus infections. It unaffected by beta-lactamase, an enzyme responsible for the resistance of certain bacteria to penicillin. However, it is not effective against MRSA, the treatment of which is difficult and requires such antibiotics as vancomycin.

Medicines by Design is the thirteenth unit in the Salters Advanced Chemistry course.
Chemical Storylines sections
[edit | edit source]- MD1 Alcohol in the body
- MD2 The drug action of ethanol
- MD3 Medicines that send messages to nerves
- MD4 Enzyme inhibitors as medicines
- MD5 Targeting bacteria
- MD6 Summary
Chemical Ideas sections
[edit | edit source]- 1.1 Amount of substance
- 13.7 Aldehydes and ketones
- 7.6 Chromatography (revision)
- 14.1 Planning a synthesis
- 14.2 Summary of organic reactions
- 6.4 Infrared spectroscopy (revision)
- 13.9 Amino acids (revision)
- 6.5 Mass spectrometry (revision)
- 6.6 Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (revision)
- 6.8 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy (revision)
Activities
[edit | edit source]- MD1.1 Aldehydes and ketones
- MD1.2 BAC determination using gas-liquid chromatography
- MD3.1 Making a toolkit of organic reactions
- MD3.2 Classifying reactions
- MD3.3 Using the toolkit to synthesise medicines
- MD3.4 Manufacturing salbutamol (Optional extension)
- MD5.1 Making and testing a penicillin
- MD5.2 A closer look at the structure of penicillins (Optional extension)
- MD6 Check your notes on Medicines by Design