Hardware Devices: Input devices
Pay special attention to devices with an orange background, you need to be able to describe exactly how they work!
Mouse
[edit | edit source]A mouse is a pointing device used on the screen of a computer. Enables the user to execute commands or issue instructions to the computer by controlling a pointer on the screen.
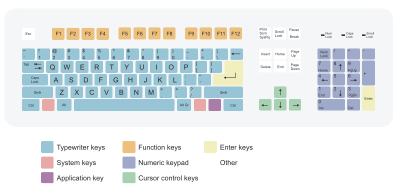
The keyboard is one of the most popular ways of inputting data information and instructions into a computer. The basic mechanical keyboard relies on springed keys being pressed down to complete an electrical circuit. This circuit then transmits a binary signal (commonly using ASCII) to the computer to represent the key pressed.

There are many different keyboard layouts, with differences between languages and countries. The most popular layout is the QWERTY keyboard. Other layouts include:
- AZERTY - for countries such as France and Belgium
- QWERTZ - for countries such as Germany and Austria
- Arabic - different values to most keys
- Ukrainian
- Chinese - laid over a QWERTY keyboard
There are variations QWERTY keyboard with the UK and the USA having very slight differences in layout. There also variations in English language keyboards such as the Dvorak layout, which followers claim to be superior to QWERTY.

Microphone connected to software that converts human speech into commands or text.
Pros
Cons


- Light is focused through the lens onto the image sensor at the back of the camera
- The image sensor is made up of an array of Red, Green and Blue photosensors, called a Bayer filter. Each sensor will only record values for that particular colour.
-
This image
-
went through this
-
like so
And became these:
-
Red
-
Green
-
Blue
3. The different colour arrays are combined to form an image and makes this:
-
Combined image
-
Applying an algorithm to merge cells
-
Notice it is not quite the same as this Original
4. Once the RGB values have been captured, they can then be stored digitally using SD or compact flash cards. Save formats include JPEG or TIFF.
Pros
Cons

Used in supermarkets,warehouses,libraries keeping track of produce etc. They allow for quick reading of product details so that prices and information can be retrieved and/or stock levels updated. However the amount of data stored in a barcode is very limited

- A laser is directed towards the barcode, scanning across it and the reflected light is captured by the reader
- The intensity of light reflected back is read by a sensor in the bar code reader
- High intensity = white bar
- Low intensity = black bar
- The pattern received is translated into a code which gives the identity of the barcode being scanned
- This code is checked against a product database and the product details displayed

To make sure that the number you have received is correct barcodes employ check digits. Read on to find out more
Pros
Cons

Used in things like multi choice question papers. The student would be given a selection of answers and then mark the ones they thought correct with a pen or pencil. When finished, the forms would be fed into a machine that would look for black marks. The position of these marks correspond to answers and the form could be marked at some speed.They can also be used for student registration
Used in scanning printed or written text into a digital format. Used by Amazon and Google to scan books.

Used to read data from bank cards and access cards. Data is stored in the magnetic, generally black, strip on the back of these cards

Used in bank cards, often known as part of 'chip and pin'. More secure than Magnetic stripes though more expensive to produce.
Used to read data without physical contact. Examples include the London Oyster Card System. Where the card has a Radio Frequency Identification(RFID) chip.

- The card is then placed above a reader and the magnetic field produced by the reader creates a current in the card's circuitry (no physical contact is required)

- This current powers a small radio transmitter that transmits a radio wave with the details about the card to the reader

- If the details of the card are legitimate (checked on database) then it lets the person through the gate

Pros
Cons


Touch sensitive
[edit | edit source]More and more devices are relying on touch technologies.
- Each of the four corners of a screen emits a uniform electric field which covers the screen
- When you place your finger on or near the screen it disrupts this field and draws current
- Measuring the amount of current pulled from each corner you can triangulate the position of the finger
Pros
Cons

Used in the design and architectural industries. This allows for people to draw on the tablet in a natural way (as they would with a pencil and paper) and for their drawing to appear on the computer.

|
Exercise: Inputs What input device might a multi-choice questionnaire writer use to input completed forms into a computer. Why? Answer: OMR - optical mark recognition software, as it will allow for input of papers with marks on them Describe the functioning of a bar-code reader: Answer:
Describe the functioning of digital camera: Answer:
Why might it beneficial for professional photographer to use a digital camera instead of a film camera? Answer:
Give two benefits of using RFID cards to pay for produce over using hard cash. What is a draw back? Answer: Give a benefit of having a touch screen phone over a phone with a hardware keyboard. Why might some people prefer a hardware keyboard? Answer: A touch screen phone would allow you to have a keyboard on the screen that could be hidden when not needed. Meaning the screen space can be used for other purposes Some people might prefer the hardware keyboard as they like to feel the response of keys being pressed and improve their typing (advances are being made in haptic technology to bring this to touch screens) Describe the functioning of a touch sensitive screen: Answer:
|
Scanners
[edit | edit source]Several of the scanners featured here record biological (bio) measurements (metrics) about human beings. Physical data such as finger prints are unique to each person.
Flat bed scanners are used to convert images and text into a digital format.

- Place the object you want to scan on the glass pane, face down
- the light moves to the start of the document and illuminates a slice
- The slice is reflected into the CCD (an array of optical sensors) where its image is stored as digital data
- the light and mirror move down to the next slice and so on
- once all the slices are completed they are put together into a digital image


The ridges and troughs on a person's finger and toes are unique to that person. Using a scanner a finger print pattern can be recorded and compared to others on a database, allowing a computer to match finger prints from crimes to a suspect, or to allow people into restricted areas.


Retina scanners are used to record the pattern of blood vessels at the back of someone's eye. As everyone has different pattern of vessels, retina scanners can be used to uniquely identify people.

By taking a picture of the blood vessels and colouring of someone's eye, we can get a unique pattern that can be used to identify individuals. People might try and circumvent this by using contact lenses

|
Exercise: Scanners Explain how a flat bed scanner works: Answer:
Give two examples of devices that collect biometric data: Answer:
|
Check digits
[edit | edit source]With input devices we have a lot of data being sent into the computer, with image capture devices we could be talking about billions of ones and zeroes. How can we make sure that they all get from the input device to the computer safely, without becoming corrupted? There are many error checking methods out there and you will cover some of them in more detail in Unit 1, however, for the moment we will learn a little about check digits:
An example of using check digits (The exam will not expect you to know this technique) is the final digit of a Universal Product Code computed as follows:
- Add the digits (up to but not including the check digit) in the odd-numbered positions (first, third, fifth, etc.) together and multiply by three.
- Add the digits (up to but not including the check digit) in the even-numbered positions (second, fourth, sixth, etc.) to the result.
- Take the remainder of the result divided by 10 (modulo operation) and subtract this from 10 to derive the check digit.
|
Example: Check Digits For instance, the UPC-A barcode for a box of tissues is "036000241457". The last digit is the check digit "7", and if the other numbers are correct then the check digit calculation must produce 7.
|
|
Exercise: Check digits Calculate the check digit for the following food item "01010101010": Answer:
Did the following barcode scan correctly: "01234567890 6"? Answer:
Therefore the check digit given, 6, shows that the code is incorrect. Why do we use check digits? Answer: We use check digits to make sure that data received has been received correctly |