A-level Mathematics/CIE/Pure Mathematics 1/Circular Measure
Radians
[edit | edit source]Defining the radian
[edit | edit source]
A radian is a unit for measuring angles. It is defined as the angle subtended by an arc that is as long as the radius. As a consequence of this, there are radians in a full circle, because the length of the circumference is times the length of the radius.
Converting between radians and degrees
[edit | edit source]Degrees are another common unit for measuring angles. There are in a circle, thus .
To convert from degrees to radians, multiply the number of degrees by .
e.g. is equal to
To convert from radians to degrees, multiply the amount of radians by .
e.g. radians is equal to
Geometric Calculations
[edit | edit source]Arc length
[edit | edit source]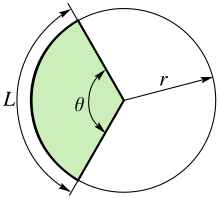
Arc length is, unsurprisingly, the length of a circular arc. This length depends on the size of the radius and the angle that the arc subtends.
We can think of an arc as a fraction of the circumference . This means that the arc length is the angle divided by a full circle times the length of the circumference: which can be simplified to .
e.g. The arc length for an arc with radius and angle is .
Sector areas
[edit | edit source]The area of a sector can be derived in a similar way: it is a fraction of the area of a circle. The area of a circle is , so the area of a sector is .

















