Wikijunior:North America/United States/The United States
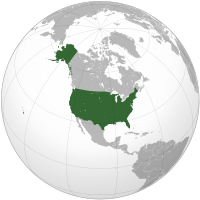
The United States of America (commonly referred to as the United States, the U.S., the USA, or America) is a federal constitutional republic made up of fifty states and a federal district. The country is situated mostly in central North America bordered by Canada to the north and Mexico to the south. The state of Alaska is in the northwest of the continent, with Canada to its east and Russia to the west across the Bering Strait. The state of Hawaii is located in the mid-Pacific. The country also possesses several territories scattered around the Caribbean and Pacific.
History[edit | edit source]
The indigenous peoples of the U.S. mainland, including Alaska Natives, migrated from Asia. They began arriving at least 12,000 and as many as 40,000 years ago. After Europeans began settling the Americas, many millions of indigenous Americans died from imported diseases such as smallpox.
In 1492, Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus reached several Caribbean islands, making first contact with the indigenous people.
Tensions between American colonials and the British during the revolutionary period of the 1760s and early 1770s led to the American Revolutionary War, fought from 1775 through 1781. On June 14, 1775, the Continental Congress, meeting in Philadelphia, established a Continental Army under the command of George Washington. The Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence, drafted largely by Thomas Jefferson, on July 4, 1776. That date is now celebrated annually as America's Independence Day. In 1777, the Articles of Confederation established a weak federal government that operated until 1789.
After the British defeat by American forces assisted by the French, Great Britain recognized the independence of the United States. A constitutional convention was organized in 1787 by those wishing to create a strong national government, with powers of taxation. The United States Constitution was changed in 1788, and the new republic's first Senate, House of Representatives, and president—George Washington—took office in 1789. The Bill of Rights was adopted in 1791.
Geography[edit | edit source]
The United States is situated almost entirely in the Western Hemisphere and it is bordered by Canada on the north and Mexico on the south. Alaska is the largest state in area it touches the Pacific on the south and the Arctic Ocean on the north. Hawaii occupies an archipelago in the central Pacific, southwest of North America. After Russia and Canada, the United States is the world's third or fourth largest nation by total area. Including only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, just ahead of Canada.
The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. The United States is home to more than 400 mammal, 700 bird, 500 reptile and amphibian, and 90,000 insect species. The United States is also home to a wide variety of plant life.

People[edit | edit source]
The United States population is projected by the U.S. Census Bureau to be 305,975,000, including an estimated 11.2 million illegal immigrants. The United States is the third most populous nation in the world, after China and India. Its population growth rate is 0.89%, compared to the European Union's 0.16%.
Languages[edit | edit source]
In 2005, about 216 million, or 81% of the population aged five years and older, spoke only English at home. Spanish, spoken by 12% of the population at home, is the second most common language and the most widely taught foreign language. Some Americans want to make English the country's official language, as it is in at least twenty-eight states. Both Hawaiian and English are official languages in Hawaii by state law. While neither has an official language, New Mexico has laws providing for the use of both English and Spanish, as Louisiana does for English and French. Other states, such as California, require the publication of Spanish versions of certain government documents including court forms.
Education[edit | edit source]
American public education is operated by state and local governments, regulated by the United States Department of Education through restrictions on federal grants. Children are required in most states to attend school from the age of six or seven until they turn eighteen, which usually brings them to the end of their schooling; some states allow students to leave school at sixteen or seventeen. Of Americans twenty-five and older, 84.6% graduated from high school, 52.6% attended some college, 27.2% earned a bachelor's degree, and 9.6% earned graduate degrees. The basic literacy rate is approximately 99%.

