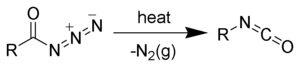Chemical Sciences: A Manual for CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test for Lectureship and JRF/Named Reactions/Curtius Rearrangement
| This page was imported and needs to be de-wikified. Books should use wikilinks rather sparsely, and only to reference technical or esoteric terms that are critical to understanding the content. Most if not all wikilinks should simply be removed. Please remove {{dewikify}} after the page is dewikified. |
The Curtius rearrangement (or Curtius reaction or Curtius degradation), as first defined by Theodor Curtius, is a chemical reaction that involves the rearrangement of an acyl azide to an isocyanate.[1][2] Several reviews have been published.[3][4]
The isocyanate can be trapped by a variety of nucleophiles. Often water is added to hydrolyze the isocyanate to an amine.[5] When done in the presence of tert-butanol, the reaction generates Boc-protected amines, useful intermediates in organic synthesis.[6][7]
Carboxylic acids 1 can be easily converted to acyl azides 3 using diphenylphosphoryl azide 2.[8][9][10]
Likewise, when the Curtius reaction is performed in the presence of benzyl alcohol, Cbz-protected amines are formed.[11]
Reaction mechanism[edit | edit source]
The first step of the Curtius rearrangement is the loss of nitrogen gas forming an acyl nitrene (2). Once formed, acyl nitrenes very quickly rearrange by migration of R-group forming the desired isocyanate (3).
Scope[edit | edit source]
In one variation called the Darapsky degradation (A. Darapsky, 1936) a Curtius rearrangement takes place as one of the steps from an α-cyanoester to an amino acid.[12]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Curtius, T. (1890). Ber. 23: 3023.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ doi:10.1002/prac.18940500125
- ↑ Smith, P. A. S. (1946). Org. React. 3: 337–449.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ doi:10.1021/cr00084a001
- ↑ Kaiser, C.; Weinstock, J. (1988), "Amines from mixed carboxylic-carbonic anhydrides: 1-phenylcyclopentylamine", Org. Synth.
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Coll. Vol., 6: 910{{citation}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ doi:10.1021/op970115w
- ↑ doi:10.1021/ol051428b
- ↑ Shioiri, T.; Yamada, S. (1990), "Diphenyl phosphorazidate", Org. Synth.
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Coll. Vol., 7: 206{{citation}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ doi:10.1021/ja00772a052
- ↑ doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97352-1
- ↑ Jessup, P. J.; Petty, C. B.; Roos, J.; Overman, L. E. (1988), "1-N-Acylamino-1,3-dienes from 2,4-pentadienoic acids by the Curtius rearrangement: benzyl trans-1,3-butadiene-1-carbamate", Org. Synth.
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Coll. Vol., 6: 95{{citation}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ http://www.chempensoftware.com/reactions/RXN051.htm